源于鸡蛋结构功能的灵感,一种便宜,高容量电池得到了发展,这种电池将促进可再生能源大规模整合应用于电网中。
钠是地球最丰富的元素之一,基于它价格低廉并且资源丰富,来自于卧龙岗大学超导&电子材料研究所(Institute for Superconducting & Electronic Materials,ISEM),复旦大学和同济大学的研究者们发明了一种高能量的钠电池。
这种钠电池具有高于现行钠电子技术两倍的容量,并达到了和普遍应用的最新锂离子电池可以比拟的水平。
像太阳能和风能,将大规模新能源整合于电网能源的关键性技术是如何将大量的能量装进小型包装中。
由于钠材料的低价,丰富和无毒特性,钠正发展为具有吸引力的电池中锂的替代物。
研究者们面临的挑战是克服钠离子的低导电性和大离子尺寸导致的电极材料在能量循环过程的大体积变化。
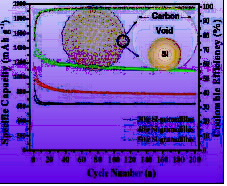
为了克服这些问题,研究者们设计了一种类似于蛋黄在蛋壳中的结构,这种微小的空心球是纳米级的,约比人类的头发还要细500倍。
这种电池能储存多少能量呢?实验测试显示所设计的这种电池具有显著的能量密度约438Wh g-1, 优于所有的钠离子电池并和最新的锂离子电池相当。
“蛋壳结构可以容纳蛋黄正极材料在碳壳中膨胀并且提高导电性及倍率性能,因为正负极间,核壳间的电子传输路径被极大地缩短”ISEM所长,窦士学教授解释道。
“在过去几年间,广泛兴趣集中在寻求更高效和更稳定的能量供应,尤其当我们在家里,工作场合甚至交通中会使用越来越多的电子设备。”
通常,大多数能源网络具有低储存容量,发电机会调整能量输出来对应网络需要。
主要研究者侴术雷博士说为了取得最好的间断性可再生能量生产就要求大规模的能量储存系统,而这种大规模的能量存储系统目前开展起来非常昂贵。
“没有高效的储存系统我们就不能实现对化石燃料的依赖性”侴博士说。
“钠离子电池作为力缆狂澜者正提供将分散式的可再生能量储存现实化的前景。”研究团队正进一步发展这一技术,为钠离子电池的商业化大规模应用铺平道路。
相关研究是与中国的复旦大学和同济大学的科学家合作,在澳大利亚的ISEM开展的。该工作近期发表在了nature communications 杂志上。http://www.nature.com/ncomms/2015/151028/ncomms9689/full/ncomms9689.html
一种通过简单工艺制备具有百香果结构的硅碳锂离子电池负极材料的研究

创新点(摘要):
作为锂受体的负极材料对锂离子二次电池的性能起着至关重要的影响。目前,石墨类碳基材料是应用最为成功的锂离子电池负极材料,但是它存在比容量低(理论比容量为372 mAh/g)、安全隐患大、倍率特性不理想等问题。因此,今后一段时期内锂离子电池负极材料研究的热点仍将主要集中于研发具有高比能量与长循环寿命的新型负极材料。硅材料,由于具有极高的比容量(> 4200 mAh/g),并且原料来源丰富、价格便宜,有望成为下一代锂离子电池负极材料之一。但是它同时也存在着导电性差,体积膨胀大等缺点,从而严重影响其倍率和循环性能。yolk-shell结构的硅碳复合材料,顾名思义就是将纳米级硅颗粒嵌入在中空的碳壳之中,同时在二者之间存在着具有尺寸可控的空隙。由于碳的掺杂使得复合物的导电性得到了改善,同时尺寸可控空隙的存在为硅的体积膨胀预留了一定的空间,既保证其在充放电过程中体积的自由变化,同时也避免了外层碳壳因此而产生的结构破坏。因此,yolk-shell结构的硅碳复合体系是现阶段解决硅负极材料体积膨胀以及导电性差最为行之有效的途径之一。
之前关于yolk-shell硅碳复合体系的制备都是通过模板法来实现的。首先在纳米硅颗粒外面沉积一层厚度可控的二氧化硅,接着在经过碳包覆以及热处理之后,利用氢氟酸将二氧化硅层刻蚀掉,得到最终的yolk-shell结构。但是这种方法存在着合成难度大,成本高,环境污染大以及合成周期长等缺点。
因此,针对这些缺点,刘华坤院士、窦士学院士课题组提出了一种以碳酸钙为模板的改性模板法制备具有百香果结构硅碳复合体系的新型合成路线。通过将纳米级硅颗粒与碳酸钙前驱体溶液共混,经过5分钟的一步共沉淀反应,就可以制备出直径在5μm左右的球形度非常好的碳酸钙/硅微球。由于纳米硅颗粒在合成过程中起到了成核剂的作用,因此纳米级碳酸钙包覆单分散硅颗粒的复合小球首先形成,之后再经过自组装过程,这些纳米级复合物小球结合形成微米级大球。在经过接下来的碳包覆之后,我们就成功得到了碳/碳酸钙/硅三相复合微球。在微球内部,每一个碳酸钙/硅纳米级小球都被碳层均匀包覆,同时在微球外部也均匀包裹着一层微米级尺寸的碳层,从而形成了一种特殊的双碳层结构。最后,不需要毒性大的氢氟酸,通过稀释的盐酸即可将碳酸钙包覆层完全刻蚀掉,得到最终的具有百香果结构的硅碳复合物。这些外表面碳包覆的百香果硅碳复合物其直径在5μm左右,同时内部由具有yolk-shell结构的硅碳纳米小球组成。通过调整硅的添加量,我们可以调控碳酸钙包覆层的厚度,从而调节yolk-shell小球中空隙的大小。经过试验证明,我们合成的最优硅碳复合负极材料在电流密度为250 mA/g的条件下,经过250次循环之后,其容量仍旧可以保持在1100 mAh/g以上。同时,在1000和2000 mA/g大倍率测试条件下,其可逆容量仍旧可以分别维持在830和700mAh/g以上。由于该材料容易量产且成本低,因此我们相信其有望为发展下一代高比能新型锂离子电池负极材料提供新的途径。相关成果发表在 Advanced Functional Materials(DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201503777)。
关键词: yolk-shell; 模板法; 碳酸钙; 负极; 锂离子电池
Lei Zhang|PhD student
Institute for Superconducting & Electronic Materials(ISEM)
Australian Institute of Innovative Materials
University of Wollongong
Squires Way, North Wollongong, NSW 2500, Australia
Mobile:0435736904
Email:lz755@uowmail.edu.au
www.isem.uow.edu.au
___________________________________________________________________
Breakthrough in sodium ion battery – affordable energy storage for integration of renewable energy to power grid
Researchers at Institute of Superconducting & Electronic Materials(ISEM), AIIM, have made a significant advance in sodium ion battery(SIB)technology by employing yolk-shell architecture with low cost materials of iron sulphide and carbon. This work, published in Nature Communication(6:8689 | DOI:10.1038/ncomms9689 |www.nature.com/naturecommunications), reports that the sodium ion battery cell consists of novel iron sulfide yolk and carbon shell as cathode and sodium as anode. This non-toxic and low-cost battery is able to remain high capacity of 488 mAh g-1 after 300 cycles. High-power density could be realized based on its outstanding rate capability(~450 mAh g-1 at 5C). Moreover,
the yolk-shell FeS@C/Na cell delivers a superior energy density of 438 Wh kg-1, exceeding those of other sodium-based batteries and comparable to those of the state-the-art lithium ion batteries. These results have enormous impact on the energy storage development as sodium is less than 10% of cost of lithium and its resource is abundant while lithium has limited reserve in the earth crust. This finding paves the way to commercialization of high performance and low cost new generation storage battery for power grid applications.
Widely spread adaption of renewable energy leads smart home, smart building and smart cities but these cannot be realised without efficient storage system. It is evident that energy storage has become game changer in the entire energy spectrum. The low-cost and reliable SIB technology will enable distributed energy supply to become reality.
“It is clear that the combination of battery and storage will reduce costs for individual consumers, and for the system as a whole” as environment minister Greg Hunt says. The minister recognises the importance of energy storage and wants to accelerate this rollout, and to promote local battery storage technology. “Australia has a large market for storage, with a high number of residential solar users that could benefit from storage technologies,” he said. “Storage is also good for grids and networks – it can smooth out energy supply, reduce peak loads, mitigate the need for network upgrades and allow utilities to better manage power supply and demand.” ms9689
The work has been carried out by researchers of ISEM including Yun Xiao Wang, Jian Ping Yang, Shu Lei Chou and Shi Xue Dou in collaboration with Dong Yuan Zhan from Fudan University and Wei Xian Zhang from Tongji University. This is testimonial for the benefit of multidisciplinary research as cross filed is very fertile.
Shi Xue DOU, PhD, DSc, FTSE
Director, Distinguished Professor
Institute for Superconducting & Electronic Materials
Australian Institute of Innovative Materials, University of Wollongong,
Innovation Campus, Squires Way, North Wollongong, NSW 2500, Australia
Tel:61-2-4221 4558, Fax:61-2-4221 5731
E-mail: shi_dou@uow.edu.au
Web:www.isem.uow.edu.au
Personal page:http://isem.uow.edu.au/staff/UOW105559.html
Google schlars page: https://scholar.google.com.au/citations?user=Y-lVMFMAAAAJ&hl=en