摘要
中国经济运行与发展已进入了新常态---速度放缓, 经济结构调整与发展动力的显著变化。 为了保持整体经济的稳定, 增加新的发展动力, 创新成为必要的手段与方向。 而为了解决目前产能过剩, 库存积压, 杠杆过高的问题,近来又提出了供给侧改革的思路与政策。 创新战略如何实施,供给侧改革应包含什么, 如何实践,各方争论颇多。 这篇文章重点讨论如何通过积极扶持和发展进口替代型制造业来进行精准性地创新与供给侧改革。并进一步讨论发展进口替代制造业的益处和相关的战略。
关键词︰ 创新; 供给侧改革; 进口替代型制造业; 经济结构。
中国经济运行与发展已进入了新常态---速度放缓, 经济结构调整与发展动力的显著变化。 为了保持整体经济的稳定, 增加新的发展动力, 创新成为必要的手段与方向。 而为了解决目前产能过剩, 库存积压, 杠杆过高的问题,近来又提出了供给侧改革的思路与政策。 创新战略如何实施,供给侧改革应包含什么, 如何实践,各方争论颇多。
这篇文章重点讨论如何通过积极扶持和发展进口替代型制造业来进行精准性地创新与供给侧改革。并进一步讨论发展进口替代制造业的益处和相关的战略。
I. 中国的进口和发展进口替代制造业的重要性和潜力
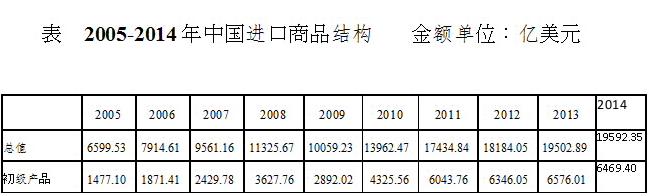
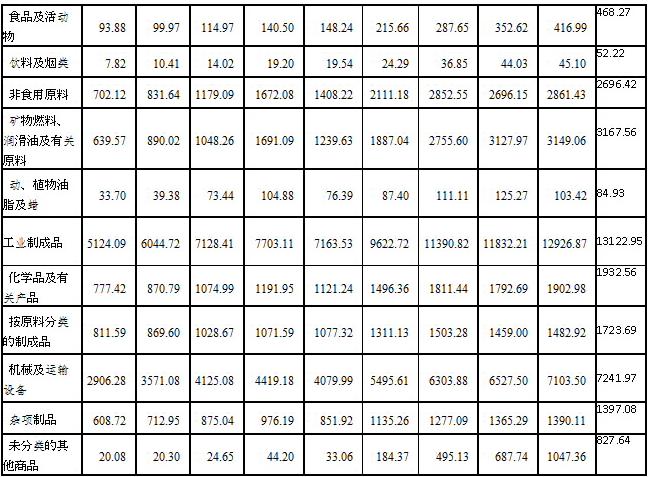
中国每年进口总额是其每年的国内生产总值的 20%左右。所有进口中,工业制成品约 67%(机器和运输设备约 36%)。如果通过开发进口替代制造业, 总的进口减少 5%或机器和运输设备进口减少为 7.5%,这将每年创造额外的 1 % GDP。
中国的先进和高科技制造业仍然是非常薄弱落后。中国全社会固定资产投资中,设备投资有2/3依靠进口,其中光纤制造设备的100%,集成电路芯片制造设备的85%,石油化工装备的80%,轿车、数控机床、纺织机械、胶印设备的70%是进口的。因此,发展进口替代制造业具有非常重要的意义和很大潜力。
II. 进口替代制造业和就业
发展进口替代制造业可以帮助解决一些就业问题。研究表明,1% 的 GDP 增长可以创造约 150 万人就业。此外,制造业的发展将有助于创造在生产制造业中服务的就业机会。
在生产制造业中存在着一些服务工作。 每$1美元的生产制造业将有$0.19美元的服务工作产生。服务性工作占制造业就业人数的30%-55%(麦肯锡2012)。进口替代制造业的发展将进一步改善服务性行业。
III. 中国制造 2025和制造业升级
中国已经制定并已实施其 “制造业 2025战略和计划”。升级和加强当前的制造工业是其重要的一环。 发展进口替代制造业将有助于实现这一目标。要成为最强的制造国之一,中国需要发展全面和先进制造业。中国怎么可以被称作最强制造大国,如果它仍依赖于进口那些先进的制造设备? 从中间和低技术制造业向上中层和高技术制造部门转移需要有明确的目标。发展进口替代制造业应是直接和明确的目标。
IV. 进口替代制造业和出口
在世界贸易中, 70%是制造业产品,30%是服务。中国的出口,其中 93%制造产品和只有 7%是服务。最近, 中国的出口遭遇严重挫折。在今年, 1 月出口跌幅为 11.2%, 2 月跌幅为25.4%。稳定和维持高的出口对我国经济增长和就业至关重要。由于显著的成本增加,中国的传统制造业的竞争力变较弱; 因此,很多工厂和公司转移到其他国家。如何恢复中国制造业出口?发展进口替代制造业可以帮助实现这一目标。 这些替代进口制造产品可以用在中国,这些产品在世界各地必定具有市场吸引力和竞争力。
V. 进口替代制造业和产品品牌
中国已成为最大出口国和最大的制造商。但出口世界的产品缺乏自主品牌。因此,中国出口的产品利润很低; 这些产品其出口并不稳定,因为进口商可以轻松地将它的生产转移到其他国家。通过发展进口替代产品和质量及技术的重大改进,中国可以逐步完善其产品的声誉和建立自己的品牌。
日本有成千上万的品牌和公司具有 100 多年历史。 德国亦相同。但中国现在有这样悠久历史的公司和品牌非常少。
VI. 进口替代制造业和创新
依照McKinsey, 有四种类型的创新--聚焦顾客的创新; 效率驱动的创新; 基于工程的创新; 与基于科学的创新。发展进口替代制造业将主要涉及效率驱动和基于工程的创新。一般来说,中国在这两种类型的创新具有优势,有许多成功的经验和例子, 像太阳能板, 高铁, 通讯器材, 和风力涡轮机等行业的创新。发展进口替代制造业是最有效的创新。
VII. 如何发展进口替代制造业
有许多原因导导制造产品的大量进口,在短时间内将无法解决或消除所有这些因素。但它应该是可能和可行的,在 3-5 年内中国可以通过发展进口替代制造业产品, 减少其总进口量的 5%。我最近到过浙江、 山东和河北省的制造企业,这些公司的主管说,他们从海外进口多数先进的机器和其他设备。他们说国内相关公司应该能够生产一些这样的先进机床和其他设备,但他们不想要这样做,因为只有一个或太少的订单。这些国内的制造商都习惯或总是倾向于生产大量的相同产品。
发展进口替代制造业应主要依靠市场机制和遵循基本的经济和市场原则和规则。自由市场竞争应是决定赢家和输家的关键。资源应该分配给那些具有竞争优势,愿意创新和改进其可以用来替代进口的产品的公司。
然而,政府应该发挥其重要的作用。应采用相关的政策, 特别是财政奖励来鼓励企业创新和改善这种需要的制造产品。中央和省级政府可以给可能所需要的产品 (这些应该从过去的海关进口记录和其他来源) 的列表。 中央政府应设立一个特别基金,协助这些产品的创新与开发。
大公司,特别是在其行业中起主导作用的国有企业应该承担其责任。他们拥有资源和能力创新和发展这些替代进口的技术和产品。这也应该是其社会责任。
应鼓励私(民)营公司,特别是中小企业参与这方面发展。他们具有好的动机; 很多的创新和新产品是来自这些企业。
公司间, 公司与研究机构之间的合作,对于这个进口替代战略的成功至关重要。这些产品发展需要很多公司和研究机构的支持和共同努力。
中国已超过美国,现在每年有世界上最多数的专利申请。但我们使用这些专利的比率却远低于世界平均水平。 中国的 R & D 支出是其 GDP 的 2%以上,其总的 R & D 支出排世界第二,仅落后于美国。但许多申请的专利及R & D 成果尚未用于生产与开发。进口替代制造产业的发展过程可以更好地激励 R & D 工作, 有关成果可直接用于制造技术和产品。
Targeted and Effective Innovations and Supply-side Reforms –Actively Supporting & Developing Import Substitution-oriented Manufacturing Industry
(This article was presented at the Int’l Think-Tank Forum 2016, Organized by the Hebei Academy of Social Sciences)
Bill Y. Chen
University of the West, Los Angeles, USA
Abstract
China's economic operation and development have entered a new norm---slow growth, changes in economic structure and changes of development-engines. In order to maintain the stability of the overall economy and add new impetus to the development of the economy, innovation has become the necessary means and direction. In order to solve the current issues of excess capacity, over-inventory, and high-leverage, a new idea and policy direction of using supply-side reforms has been proposed and discussed. How to implement the innovation strategy, what should be included in the supply-side reforms and how to practice that present many challenges and arguments.
This article focuses on how to effectively innovate and conduct the supply-side reforms through actively supporting and developing an import-substitution-oriented manufacturing industry. It further discusses benefits of developing the import substitution manufacturing industry and relevant strategies.
Keywords: Innovations, Supply-side Reforms, Import Substitution Manufacturing, Economic Structure.
China's economic operation and development have entered a new norm---slow growth, changes in economic structure and changes of development-engines. In order to maintain the stability of the overall economy and add new impetus to the development of the economy, innovation has become the necessary means and direction. In order to solve the current issues of excess capacity, over-inventory, and high-leverage, a new idea and policy direction of using supply-side reforms has been proposed and discussed. How to implement the innovation strategy, what should be included in the supply-side reforms and how to practice that present many challenges and arguments.
This article focuses on how to effectively innovate and conduct the supply-side reforms through actively supporting and developing an import-substitution-oriented manufacturing industry. It further discusses benefits of developing the import substitution manufacturing industry and relevant strategies.
I. China’s imports and importance and potential of developing import-substitution manufacturing industry
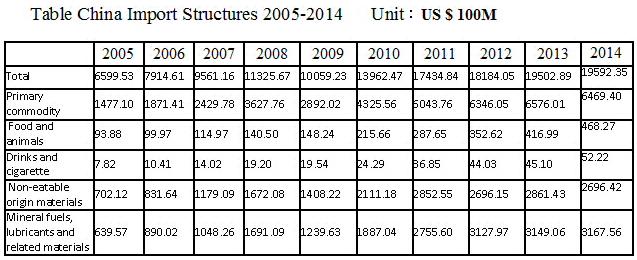
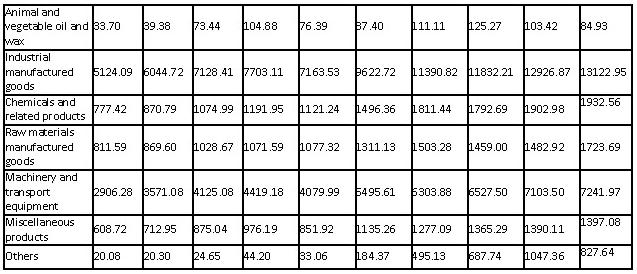
Currently, China’s total annual import is about 20% of its annual GDP . Among all imports, industrial manufactured products are about 67%(the machinery and transportation equipment about 36%). If the total import can be reduced by 5% through developing the import-substitution manufacturing, or the machine and transportation equipment import can be reduced by 7.5%, that will generate an extra 1% GDP annually.
Although China has surpassed the US and become the largest manufacturing country, China is still very weak in advanced and high-tech manufacturing. China imports two-thirds of the key engineering equipment for its fixed asset investment each year. Virtually 100% of its fiber-making equipment is imported; 85% of chip-making equipment, 80% of petroleum and chemical equipment and 70% of machine-tools are also imported. Therefore, developing the import substitution manufacturing in China is very important and also has large potential.
II. Import-substitution manufacturing and employment
Developing import-substitution manufacturing can help solve some employment
problems. According to some study, 1% GDP growth can generate about 1.5 million people’s employment. Furthermore, developments of manufacturing industry will help generate employment opportunities in services.
There are service jobs in the manufacturing industry. Every dollar of manufacturing output needs about $0.19 of service input. Service type activities make up 30-55% of manufacturing employment(McKinsey(2012)). Developments of import-substitution manufacturing will further improve service industry as well.
III. China Manufacturing 2025 and upgrading of manufacturing industry
China has developed and been implementing its Manufacturing 2025 Strategy and
Plan. Upgrading and strengthening its current manufacturing industry is an important part of that. Developing import-substitution manufacturing industry will help achieve this goal. In order to be one of the strongest manufacturing countries, China needs to develop and have comprehensive and advanced manufacturing sectors. How can China be called the strongest manufacturing country if it still relies on imports of those advanced manufacturing equipment?
Transferring from the middle and low-level technology manufacturing sectors to the high and up-middle-level technology sectors needs to have the clear targets. Developing import-substitution manufacturing industry should be direct and clear targets.
IV. Import-substitution manufacturing and export
Among world trade, 70% are manufacturing products and 30% are in services. Among
China’s exports, 93% are manufacturing and only 7% are in services. Recently, China’s export has been suffering. In this year, export was down by 11.2% in January and 25.4% in February. Stabilizing and maintaining high-volumes of exports is crucial to China’s economic growth and employment. Due to significant cost increases, China’s traditional manufacturing sectors are less competitive; as a result, many manufacturing facilities and companies have moved to other countries. How to renew China’s manufacturing exports? Developing import-substitution manufacturing industry can help achieve that. These import-substitution manufacturing products can be used in China, these must be attractive and competitive in the world markets.
V. Import-substitution manufacturing and product brands
China has been the largest exporter and largest manufacturers. But it lacks its own
brands of exported products in the world. As a result, China earns very low profit margins from these products and its exports are not stable since importers can easily shift its productions to other countries. By developing import substitution products and significant improvements of quality and technologies of these products, China can gradually improve reputations of its products and establish its own brands.
Japan has thousands of companies and product brands with over 100 years of history. Germany is the same; but China now has very few such long history companies and brands.
VI. Import-substitution manufacturing and innovations
According to McKinsey, there are four types of innovations--consumer-focused innovations; efficiency-driven innovations; engineering-based innovations; and science-based innovations. Developing import-substitution manufacturing industry will mainly involve efficiency-driven and engineering-based innovations. Generally speaking, China has advantages in these two types of innovations and has had many successful experiences and examples. Developing import-substitution manufacturing will be the most effective innovations.
VII. How to develop import-substitution manufacturing industry
There are many reasons for large imports of manufacturing products, and it will be
impossible to solve or eliminate all of these causes in a short time period. But it should be possible and feasible that in 3-5 years China can reduce 5% of its total imports through development of import-substitution manufacturing products. I visited manufacturing companies in Zhejiang, Shandong, and Hebei Provinces recently where the executives of these companies said that they imported most advanced machines and other equipment from overseas. They said that domestic relevant companies should be able to produce some of these advanced machine tools and other equipment but they did not want to do so because there will be only one or too few orders. These domestic manufacturers are accustomed to or always prefer to produce large amounts of same products.
Developing import-substitution manufacturing should mainly rely on the market system and follow basic economic and market principles and rules. Free market competition is the key to decide the winners and losers. Resources should be allocated to companies that have competitive advantages and are willing to innovate and improve its products that can be used to substitute the imports.
Governments should also play important roles as well. Relevant policies and particularly financial incentives should be used to encourage companies to innovate and improve these needed manufacturing products. Central and provincial governments can give a list of possible needed products.(These should be available from the past custom records of imports and others sources). The central government should set up a special fund to assist these products’ developments.
Large companies, particularly state-owned enterprises(SOEs)that are dominant in its
industry/sector should take its responsibilities. They have resources and capabilities to innovate and develop these import-substitution technologies and products. That should also be its social responsibilities.
Private companies, particularly SMEs, should be encouraged to be involved in this
strategy. They are well motivated and many innovations and new products come from these companies.
Cooperation among companies and between companies and research institutions
is also crucial for the success of this import-substitution strategy. These product developments need many companies’ and research institutions’ support and joint ventures.
China has surpassed the US and now has the most patent applications in the world
each year. But our usage rate of these patents is much lower than the world average. China’s R & D spending is above 2% of its GDP, and its total R&D spending ranks number two in the world, just behind the US. But many R&Ds are not used yet in the productions. The process of developing import-substitution manufacturing industry can better motivate R&D work, and its relevant outcomes can be directly used in manufacturing.
参考文献
Baumol, William J(1967), “ Macroeconomics of Unbalanced Growth:the Anatomy of Urban Crisis.” Am Econ Rev 57:pp. 415-426.
Chen, Yueyun(Bill)(2015), “China’s Path to the Sustainable, Stable and Rapid Economic Development:From the Largest to the Strongest Manufacturing Country; Journal of World Economic Research, August;
Chen, Yueyun(Bill) (2015), “ International Comparisons of the Service Industry,” 25th Int’l Conference on Pacific Rim Mgt, Los Angeles, July;
Chen, Yueyun(Bill)(2011), “ Why There are Less China-made-Products in US Supermarkets?” Yazhou Zhoukan(HK Asian Weekly), June 11th.
Global Institute(2012), “Manufacturing the Future:The Next Era of Global Growth and Innovation,” McKinsey & Company.
National Bureau of Statistics of China, various years.
Huang, Yasheng(2010), “Debating China’s Economic Growth:The Beijing Consensus or the Washington Consensus,” Academy of Management Perspective, pp31-48.
Li, Lanqing(2009); Breaking Through:The Birth of China's Opening-Up Policy. Oxford and New York:Oxford University Press.
Lin, Justin Yifu, Cai, Fang and Li, Zhou(2003); The China Miracle:Development Strategy and Economic Reform; Hong Kong:Chinese University Press.
Lin, Justin Yifu(2012), The Quest for Prosperity:How Developing Countries Can Take Off, Princeton:Princeton University Press.
Zhu, Xiaodong(2012); “Understanding China's Growth:Past, Present, and Future,” The Journal of Economic Perspectives 26. 4 :103-124.
World Economic Forum(2012), “ The Future of Manufacturing Report:Manufacturing for Growth Strategies for Driving Growth and Employment,” World Economic Forum.
<<新华网>>(3/14/2015), “四大怪相折射中国制造业之痛”.
<<新华网>>> 王攀、陈钢等(7/27/2015), “工业精神与制造文明的缺失 --“中国制造”的痛点”.
<<美国世界日报>>陈岳云(7/22/2012), “刺激中国经济发展调整产业结构之对策”.
<<美国世界日报>>陈岳云(4/22/2012), “中国国企改革应否走私有化之路?”
<<美国侨报 >> 陈岳云(3/12/2012), “中国制造业基地转移迫在眉睫”.
<<中国青年报>>(12/27/2011), “中国制造业超美国跃居世界第一 虚名背后存隐患”.